Calculation of the number of Theoretical Plates (half-height method, used by Tosoh)
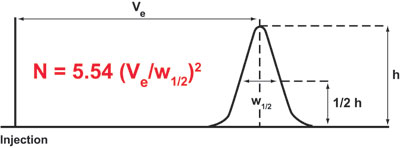
Where:
N = Number of theoretical plates
Ve = elution volume or retention time (mL, sec, or cm)
h = peak height
w1/2 = width of the peak at half peak height (mL, sec, or cm)
Calculation of the number of Theoretical Plates (USP method)
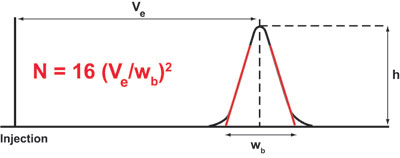
Where:
N = Number of theoretical plates
Ve = elution volume, retention time or retention distance (mL, sec, or cm)
h = peak height
wb = width of the peak at the base line (mL, sec, or cm)
Calculation of peak Asymmetry Factor (used by Tosoh)
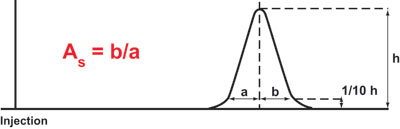
Where:
As = peak asymmetry factor
b = distance from the point at peak midpoint to the trailing edge (measured at 10% of peak height)
a = distance from the leading edge of of peak to the midpoint (measured at 10% of peak height)
Calculation of Tailing Factor (USP method)
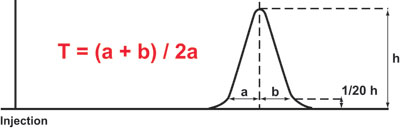
Where:
T = tailing factor (measured at 5% of peak height)
b = distance from the point at peak midpoint to the trailing edge
a = distance from the leading edge of the peak to the midpoint
Calculation of the Height Equivalent to a Theoretical Plate (HETP)

Where:
H = Height equivalent of a theoretical plate
L = Length of the column
N = Number of theoretical plates
Dimensions: when using HPLC or UHPLC columns, H is usually expressed in µm.
Calculation of Reduced Plate Height (h)
Giddings introduced dimensionless parameters for H and also for the linear velocity. Dimensionless parameters allow the direct comparison of the efficiency of two or more columns packed with different particle size packing materials. According to the theory, a well packed column should have a reduced plate height (h) in the range of 2-3 at a reduced velocity (v) of about 3. Here we only provide the formula for h.

Where:
h = reduced plate height (sometimes referred to as the number of band widths)
H = height equivalent of a theoretical plate (µm)
dp = mean particle size (µm)
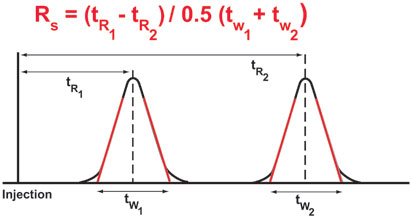
Calculation of Chromatographic Resolution